Last Updated on November 8, 2022
Fruit trees produce ethylene gas, which causes fruits to ripen faster. This is why they should be kept away from other plants. What exactly does ethylene do to fruit?
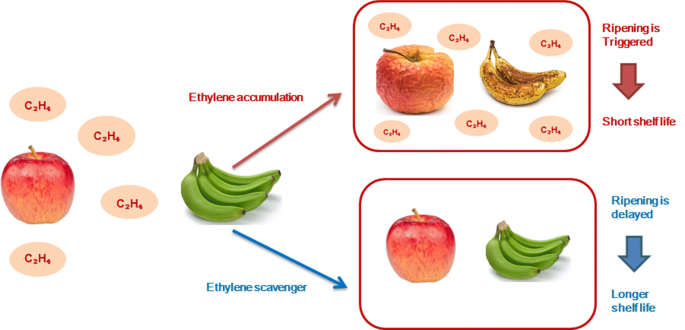
Ethylene is a natural hormone produced by plants during the ripening stage of fruit development. The hormone helps soften the skin and increase sugar levels. Fruit growers often apply ethylene to accelerate the ripening process.
Ethylene Producing Fruits [Most Gas + How to Test]
Fruit trees produce ethylene gas. Ethylene gas is an odorless colorless gas that is heavier than air. It is also known as “ethylene” or “ethene.”
The amount of ethylene in the atmosphere depends on temperature and humidity. At higher temperatures and lower humidities, more ethylene is present in the air.
How can you tell if your fruit tree produces ethylene?
You can test for ethylene production by placing a small piece of paper over the stem of the plant. If there are no leaves under the paper, then it means the plant is producing ethylene.
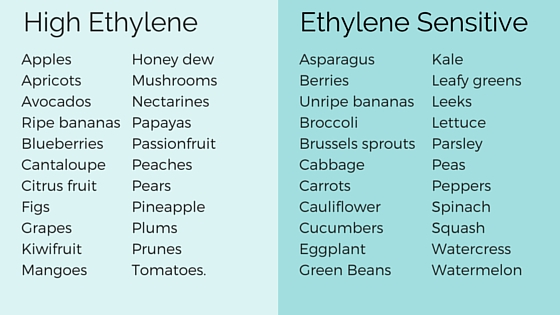
Ethylene gas is produced during ripening of fruits. It helps soften the flesh and promotes the release of juices from the cells. This process is called “ripening”. Fruits such as apples, peaches, plums, apricots, nectarines, cherries, strawberries, raspberries, blueberries, blackberries, grapes, kiwis, melons, tomatoes, pineapple, mangoes, avocados, citrus fruits, figs, guavas, passionfruit, papaya, and many others produce ethylene gas.
Do All Fruits Give Off Ethylene?
Not all fruits give off ethylene. Some fruits like bananas, pineapples, and watermelons don’t produce any ethylene. Other fruits such as apples, pears, oranges, lemons, limes, grapefruits, tangerines, and persimmons have low amounts of ethylene.
Yes, all fruits give off ethylene gas during ripening. It is released from the fruit cells as they begin to soften. This process continues until the fruit reaches maturity. As soon as the fruit matures, the cell walls break down and the fruit softens. During this stage, the fruit gives off ethylene gas.
Ethylene producing foods
Some fruits contain high concentrations of ethylene. These include:
Apples – Apples are one of the most common fruits grown worldwide. They are available year-round and are used in both fresh and processed forms.
Apricot – Apricots are a type of stone fruit with yellow flesh. They are usually eaten raw or cooked.
Avocado – Avocados are green when unripe but turn brown when ripe. They are rich in monounsaturated fats and fiber.
Banana – Bananas are large oval shaped fruits. They grow on tropical plants and are mostly consumed raw.
Blueberry – Blueberries are small berries that are sweet and tart at the same time. They are very popular among children because of their bright colors.
Cherry – Cherry is a red berry that grows on shrubs. It has a sour taste and is commonly used in pies and jams.
Citrus – Citrus fruits are widely cultivated around the world. They are available in different sizes and shapes.
Grape – Grapes are roundish fruits that come in various colors. They are juicy and delicious.
Kiwi – Kiwi is a small fruit that looks similar to a tomato. It is often served in salads.
Mango – Mangoes are large fruits that grow on trees. They are sweet and juicy.
Melon – Melons are large fruits that grow underground. They are sweeter when they are ripe.
Orange – Oranges are orange colored fruits that grow on bushes. They are sweet and sour tasting.
Which Fruits Produce the Most Ethylene?
The following fruits produce more ethylene than other fruits:
Apple – Apple is an apple tree which produces a variety of fruits including apples. The fruit contains a lot of sugar and acidity.
Pear – Pears are pear shaped fruits that grow on trees and bushes. They are sweet, juicy, and flavorful.
Pineapple – Pineapples are fruits that grow on tall trees. They are sweet, crunchy, and juicy.
Tomato – Tomatoes are fruits that grow on vines. They are sweet, acidic, and juicy.
Watermelon – Watermelons are fruits that grow on bushes and trees. They are sweet when ripe.
How to control ethylene production in fruits and veges?
There are many ways to reduce the amount of ethylene produced by fruits and vegetables. You can use these methods to help prevent your fruits and veggies from spoiling too quickly.
1) Use airtight containers
2) Store fruits and veggies in the refrigerator
3) Wash fruits and veggies before storing them
4) Keep fruits and veggies away from each other
5) Don’t store fruits and veggies near any strong smelling foods such as onions, garlic, or spices
6) Don’t leave fruits and veggies out for long periods of time
7) Don’t wash fruits and veggies after you have cut them up
8) Don’t put fruits and veggies in plastic bags
9) Don’t let fruits and veggies sit out in direct sunlight
10) Don’t keep fruits and veggies in the freezer
How to Test for Ethylene Gas in Fruits?
You can test for ethylene gas using one of the following methods:
1) Place a piece of paper over the top of a glass jar filled with water. If there is no smell, then the jar does not contain ethylene gas.
2) Put a slice of bread into a sealed container. If it starts to mold, then the container probably contains ethylene gas.
3) Put a piece of cheesecloth into a sealed container. Cheesecloth absorbs odors, so if the cloth smells like vinegar, then the container probably holds ethylene gas.
4) Put a piece of aluminum foil into a sealed container. Aluminum foil will absorb odors, so if it smells like vinegar, then it probably holds ethylene gas inside.
5) Put a piece of cotton ball into a sealed container. Cotton balls absorb odors, so they may be used to detect ethylene gas.
6) Put a piece of rubber band around a sealed container. Rubber bands absorb odors, so it may be used to detect odors.
Do you want to produce ethylene gas?
This is a very useful chemical used in making plastics and other materials.
However, if you don’t know how to test ethylene producing fruits, then you might end up wasting time and money.
Here’s a article explaining how to test ethylene production in fruits.
In this article I’m going to explain you how to test ethylene gas production in fruits.
Do All Fruits Give Off Ethylene?
Ethylene is a gas produced during ripening of fruits. It is released from the fruit cells and helps in the process of ripening. This gas is responsible for making the fruit soft and sweet. It is produced by the enzyme polygalacturonase which breaks down the cell walls of the fruit. How To Check For Ethylene Production In Fruits? You can check if any fruit produces ethylene by placing the fruit in a sealed plastic bag and leave it overnight. If the fruit does not produce ethylene after 24 hours, it indicates that the fruit is not producing ethylene. Fruit Which Do Not Produce Ethylene: Apples Pears Grapes Oranges Bananas Kiwis Peaches Plums Strawberries Cherries Mangoes Melons Watermelon Avocados Tomatoes Eggplant Sweet Potatoes Carrots Onions Garlic Lemons Limes
Climacteric fruits
Climacteric fruits are those that undergo ripening when they reach maturity. These fruits usually have a peak of ripeness around the end of summer and start to lose their flavor and texture. Examples of climacteric fruits are tomatoes, peaches, apricots, plums, apples, mangoes, strawberries, cherries, kiwifruits, melons, and grapes.
Non-climacteric fruits
Non-climacteric fruit such as bananas, pineapples, oranges, lemons, limes, grapefruits, tangerines, and avocados are not affected by the climacteric process. These fruits remain firm and juicy even after reaching maturity.
Ethylene
Ethylene gas is a natural plant hormone produced by ripening fruits and vegetables. It is responsible for the ripening of many fruits and vegetables. It helps to soften the flesh of these fruits and vegetables. It also helps to attract insects and birds to eat the fruit.
Ethylene sensitive foods
Ethylene sensitive foods are foods that are sensitive to ethylene gas. These foods are usually fruits such as apples, peaches, tomatoes, strawberries, cherries, plums, nectarines, apricots, oranges, grapefruit, melons, kiwis, figs, and bananas. When these foods are exposed to ethylene gas, they begin to ripen prematurely. This is because ethylene gas is produced naturally by plants during photosynthesis. It is released into the air from the leaves and stems of plants. The gas diffuses throughout the plant and travels to fruit buds and flowers where it triggers ripening.
Which Fruits Produce the Most Ethylene?
Fruits produce ethylene gas in different amounts. Apples, peaches, pears, and grapes produce the highest levels of ethylene gas. Other fruits that produce high levels of ethylene gas are mangoes, pineapple, and kiwifruit.
How to control ethylene production in fruits and veges
To reduce the level of ethylene produced by fruits and vegetables, you can place them in a sealed plastic bag and store them in the refrigerator. This will help to slow down the ripening process.
How to Test for Ethylene Gas in Fruits
To test for ethylene gas in fruits, take a piece of fruit and put it into a glass jar. Then, fill the jar with water and place the lid on top. Leave the jar overnight. In the morning, check if any bubbles have formed. If yes, then the fruit contains ethylene gas. How to Control Ethylene Production in Vegetables
What Does Ethylene Do to Fruit?
Fruit ripens faster after exposure to ethylene gas. This is because ethylene promotes cell division in the fruit. It also stimulates the growth of new cells. As a result, the fruit grows larger and sweeter. Ethylene production in vegetables is different from ethylene production in fruits. Ethylene production in vegetables is not related to ripening. Instead, it is caused by stress factors such as cold temperatures, drought conditions, and nutrient deficiency.
What is the effect of ethylene on other fruits and vegetables?
Ethylene affects many types of plants. It helps stimulate the growth of flowers and buds. It also speeds up the ripening process in tomatoes, bananas, strawberries, apples, peaches, nectarines, plums, grapes, and melons.
How do you test for ethylene in fruit?
To check if fruit contains ethylene gas, place a piece of fruit into a sealed plastic bag. Place the bag in a warm area 70 degrees for 24 hours. After 24 hours, open the bag and smell the air. If the fruit smells sweet, it does not contain ethylene gas. If the fruit smells sour, it probably contains ethylene gas.
How do you remove ethylene gas from fruit?
You can remove ethylene gas from fruits by placing them in sealed containers with oxygen. This process takes about two days.
How do you measure fruit decay?
To test for ethylene gas, you need to put a piece of paper in an unsealed container with a ripe fruit and leave it overnight. If the paper turns yellow after 24 hours, the fruit contains ethylene.
How do you test for ethylene?
Ethylene gas is produced by plants during ripening. Ethylene gas is released into the air and is responsible for many processes such as ripening fruits, rotting vegetables, and causing plant diseases. To detect ethylene gas, you can place a piece of paper in a sealed container with a ripe fruit. After 24 hours, the paper will turn yellow if the fruit contains ethylene gas.
How do you test for ethylene gas in fruits?
Fruit decay is measured using a scale known as the “Decay Scale”. It is used to determine how ripe fruits are. Fruit decay is measured using a Decay Scale. The scale ranges from 1 to 9. A score of 1 indicates that the fruit is still firm and green. A score of 2 indicates that the fruit is soft but not rotten. A score of 3 indicates that the fruit is slightly decayed. A score of 4 indicates that the fruit is very decayed. A score 5 indicates that the fruit is completely decayed. A score 6 indicates that the fruit is partially decayed. A score 7 indicates that the fruit is only partly decayed. A score 8 indicates that the fruit is almost fully decayed. A score 9 indicates that the fruit is rotten.
What absorbs ethylene gas naturally?
Ethylene gas is released from plant cells during fruit ripening, flower blooming, and leaf aging. This process is called autocatalytic decomposition. During this process, ethylene gas is released from the plant cell.
How is ethylene gas released?
Plants absorb ethylene gas naturally. It is produced during photosynthesis. Ethylene gas is used by plants to regulate growth and development. It is released into the atmosphere during ripening of fruits and vegetables, flowering, and senescence.
In summary, the most ethylene producing fruits are mango, banana, and passion fruit. The highest ethylene producing fruits have a high sugar content and a high water content.
- How to Prolong the Life of Your Kitchen Appliances - December 22, 2024
- How Long does Yogurt Take to Freeze - May 5, 2023
- Top 10 best restaurants in Montana - May 1, 2023
